Smart Connectivity in the IoT Era: Engineering Terminal Blocks for Smart Devices
From smart thermostats and building sensors to home automation hubs, the new generation of connected devices is built on one foundation—reliable electrical connectivity.
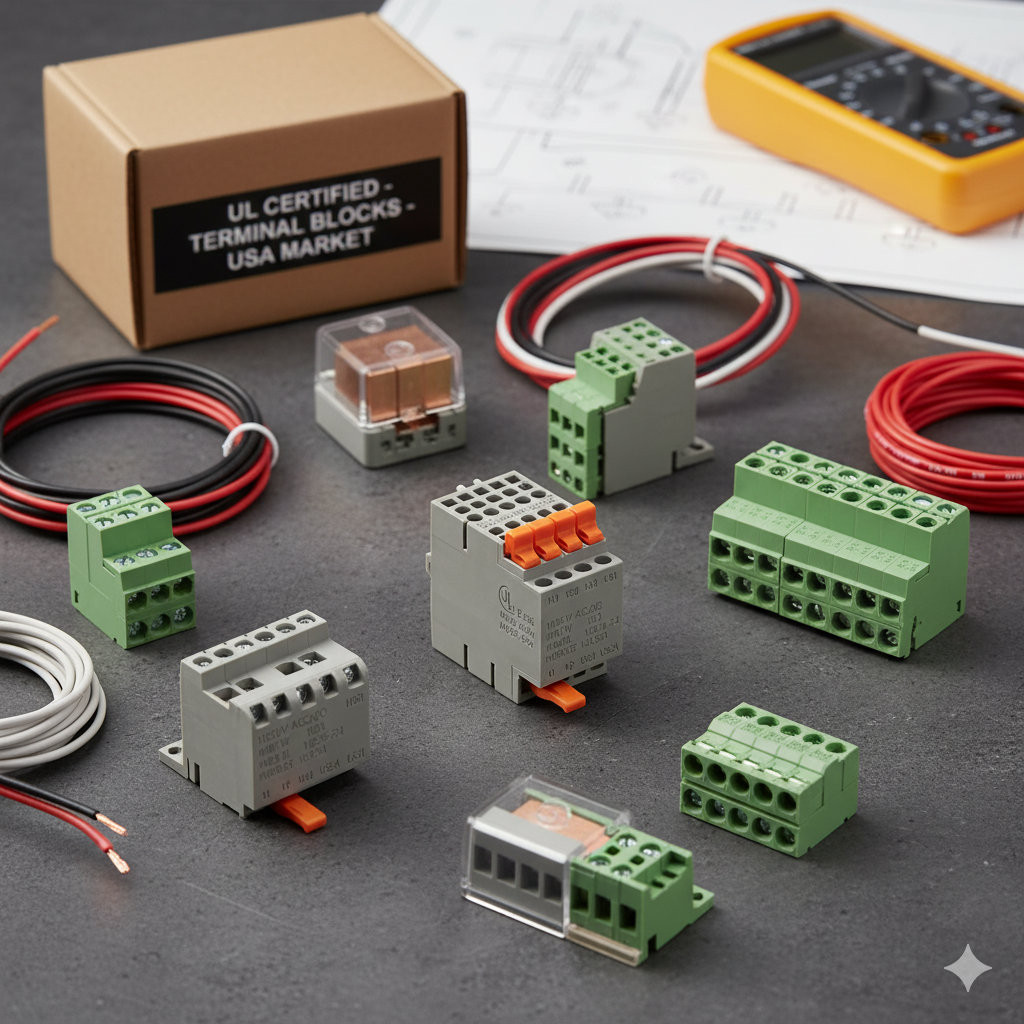
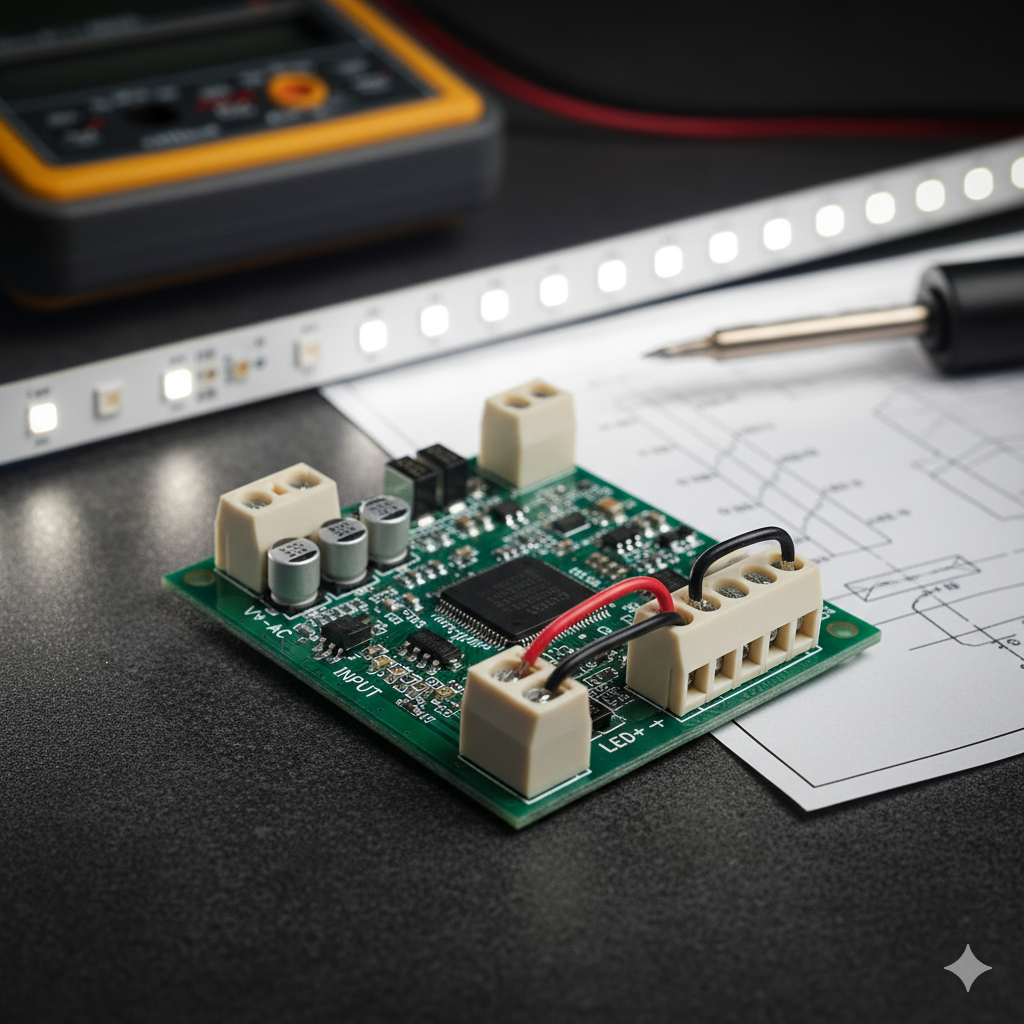
As designs become smaller and more integrated, wiring components like terminal blocks for smart devices must do more with less: carry power safely, manage micro-signals precisely, and fit inside ever-tighter enclosures.
That’s where engineering meets design. The evolution of modern terminal blocks is quietly shaping how smart devices perform and how long they last.
Smaller Components, Bigger Challenges
In the world of IoT hardware, space is the most expensive commodity.
Every millimeter of circuit board counts. Traditional terminals—bulky and screw-driven—simply can’t keep up with today’s compact PCBs.
To address this, modern terminal blocks are engineered to be small, strong, and stable:
-
Mini-pitch connectors (2.5–3.81 mm) for dense wiring on limited PCB space.
-
Low-profile housings that handle high temperatures during reflow soldering.
-
Gold-plated contacts for consistent microcurrent transmission.
-
Built-in strain reliefs that prevent conductor stress during assembly.
These features aren’t just about saving space—they’re what make real-time data collection and low-voltage control reliable across millions of smart devices.
Material Engineering: The Backbone of Reliability
When every device is expected to run 24/7, materials can’t fail. The performance of a terminal block depends on the science behind its construction.
| Component | Material | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Housing | PA66 or LCP (UL94 V-0) | Heat-resistant, halogen-free insulation |
| Contacts | Copper alloy, nickel/gold plated | Stable conductivity at low voltage |
| Clamp system | Stainless spring steel | Maintains consistent pressure |
| Base | Reinforced PC | Supports mechanical strength during assembly |
Each terminal goes through rigorous thermal shock, vibration, and aging tests under IEC 60998 and UL 1059 standards—ensuring that even in humid or hot environments, your smart devices keep working as intended.
From Traditional to Intelligent: A Shift in Design
| Aspect | Conventional Terminal | Smart Device Terminal |
|---|---|---|
| Pitch | 5.08–7.62 mm | 2.5–3.81 mm |
| Installation | Manual screw | SMT / Push-in system |
| Current Range | Power only | Power + signal integration |
| Size | Bulky, external mount | Compact, PCB-level integration |
| Focus | Durability | Efficiency & flexibility |
The shift is clear: instead of just “connecting wires,” terminal blocks are now part of a complete electronic ecosystem, integrating data, power, and signal pathways into one intelligent design.
How Terminal Blocks Keep Smart Devices Running Smoothly
In smart device engineering, reliability is measured in consistency—every signal must transmit cleanly, every joint must resist fatigue.
That’s why the latest designs focus on:
-
Noise resistance and EMI protection to keep data lines interference-free.
-
Quick plug-in modules that reduce assembly time and support automated production.
-
Hybrid terminals combining power and communication lines in one unit.
-
Vertical and horizontal mount options for space optimization.
-
Durability tested for over 100 insertions without contact wear.
Each detail adds up to devices that stay connected, responsive, and energy-efficient.
Real-World Applications in Smart Technology
| Device Type | Wiring Function | Recommended Terminal |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Thermostats | Power + low-voltage control | PCB terminal 3.5 mm |
| IoT Gateways | Data and signal integration | Pluggable terminal 2.5 mm |
| Security Systems | Sensor communication | Screwless spring clamp |
| Smart Lighting Panels | Control and power | Compact barrier block |
| EV Charging Modules | DC transfer & monitoring | 7.62 mm high-current block |
Across applications, the priority is the same—stable performance in tight spaces without sacrificing safety or maintainability.
Selecting the Right Terminal Block for Smart Devices
Choosing the right connector may seem small, but it defines how your product performs in the field.
Here’s what engineers and product designers should look for:
-
Verify UL and CE certification for mixed-voltage environments.
-
Opt for spring-cage clamps in automated or vibration-prone assembly lines.
-
Keep contact resistance below 15 mΩ to ensure signal integrity.
-
Request environmental test data (thermal, humidity, mechanical stress).
-
For volume production, prefer suppliers offering custom pin configurations and OEM marking.
A good supplier doesn’t just provide parts—they provide confidence in every connection.
FAQs from IoT Hardware Engineers
Q1: How do these terminal blocks manage heat in small enclosures?
A: Through optimized copper geometry and high-temperature housing materials that prevent warping.
Q2: Can they handle both power and data lines?
A: Yes, hybrid terminal designs isolate power and signal paths within the same housing.
Q3: Are they compatible with automated soldering lines?
A: Absolutely. Reflow-safe LCP and PA66 materials make them suitable for SMT assembly.
Q4: How long do they last in field conditions?
A: When correctly mounted, they can maintain stable contact for 10+ years under rated conditions.
Designing the Future of Smart Connectivity
In the fast-moving world of connected devices, reliability is invisible—until it fails.
Terminal blocks for smart devices are the unsung heroes behind that reliability, quietly ensuring that data, power, and control flow without interruption.
Zhongbo continues to push forward with high-precision, compact terminal blocks engineered for the IoT age—combining certified materials, modular designs, and flexible OEM customization.
For specifications, partnerships, or project support, visit our homepage or contact us.





